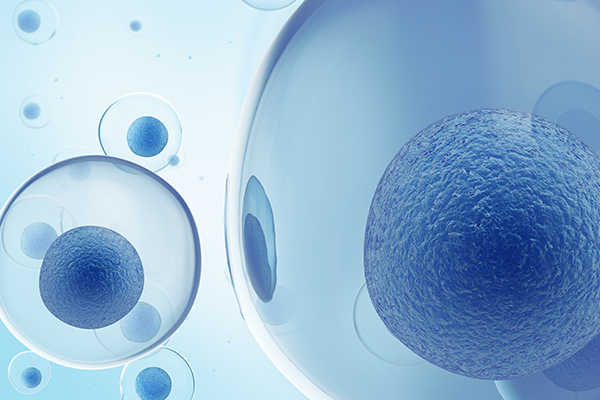
Stem Cells
Stem cells have two defining capabilities that make them unique: first they are able to generate new copies of themselves (self-renewal) and second, they can differentiate a specific function such as blood cells, brain cells or bone cells. There are different levels of stem cell potency: totipotent (able to give rise to an entirely functional organism), pluripotent (able to give rise to all tissue types) and multipotent (able to differentiate into a limited range of cells within a tissue type).
Multipotent stem cells can be found in adult humans. Adult stem cells play an essential role in the daily health and maintenance of our body - for example 200 billion red blood cells are created each day in the body from haematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) found in the bone marrow.
Recently, a new (artificial) type of stem cell was developed: Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (IPSC). IPSC's can be derived from adult somatic cells and have similar pluripotent properties to Embryonic Stem Cells (ESC) - without involving the controversial use of embryos. Stem cells may be promising tools for treating diseases in which a cellular and tissue destruction occur. Stem cells could for example provide healthy cells to replace cells that were damaged by a stroke.
Multipotent stem cells can be found in adult humans. Adult stem cells play an essential role in the daily health and maintenance of our body - for example 200 billion red blood cells are created each day in the body from haematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) found in the bone marrow.
Recently, a new (artificial) type of stem cell was developed: Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (IPSC). IPSC's can be derived from adult somatic cells and have similar pluripotent properties to Embryonic Stem Cells (ESC) - without involving the controversial use of embryos. Stem cells may be promising tools for treating diseases in which a cellular and tissue destruction occur. Stem cells could for example provide healthy cells to replace cells that were damaged by a stroke.
Public Health: Regenerative medicine using stem cells could replace damaged cells after a spinal cord injury, a stroke and degenerative neurological diseases. It can also replace damaged myocardial cells after a heart attack. In the near-future, scientists hope to grow synthetic organs and tissues from stem cells for transplantation.
Drug Development: The pharmaceutical industry is increasingly adopting stem cells for drug development to test the safety and quality of investigational drugs before using them for people.
Disease Modelling: Scientists could use stem cells derived from patients to model the mechanism of disease development in the laboratory and better understand what goes wrong.
Totipotent/Pluripotent/Multipotent, Adult stem cells, Embryonic Stem Cells (ESCs), Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), Regenerative medicine, Bioengineering, Synthetic organs
Related Topics

Biodiverzita : život Na Zemi
Biodiverzita (nebo také biologická diverzita) je produktem evoluce, která přinesla a stále dále rozvíjí rozmanitost druhů. Biodiverzita je potřebná...
READ MORE
 EN
ENClean Water
Clean water is a human right but even today not everyone has access to it. Increased access to clean water is essential for improving living standa...
READ MORE
 EN
ENEnergy Efficiency
No construction lasts forever and at a moment in time, every building needs to be renovated and repaired. Maintenance can however be performed in m...
READ MORE
Otevrené Téma Stem
Matematika, prírodní a technické vedy (anglicky STEM: Natural Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics) pokrývají mnoho ruzných zajímavých ...
READ MORE
 EN
ENPrenatal Development
Prenatal development refers to the process in which a baby develops from a single cell into an embryo and later a foetus. The average length of tim...
READ MORE